Common symptoms of meningitis include: fever, headache, fatigue, blurred vision, pain in the ears or head, and difficulty breathing. Other symptoms include: nausea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, loss of memory, numbness or tingling in the hand or feet, a discharge resembling cottage cheese, muscle aches, and problems with urination.
Common symptoms of meningitis may also include rash, which is usually reddish or purplish in color and has a fever-like feel. Infants with meningitis may also have other symptoms. In infants, babies with meningitis may experience:
If you believe that you or your baby is suffering from symptoms of meningitis, you should contact a doctor immediately. You should also stay away from the contaminated area where the illness occurred and avoid getting any contaminated objects into the mouth. If you see any red bumps on your children's heads, wash them thoroughly with soap and water.
Babies usually recover from the illness within a few days to a week. However, if your child continues to have symptoms of meningitis after seven days of recovery, you should see a doctor. If the baby's symptoms of meningitis persist after two weeks, then you should get your baby tested for meningitis. If you suspect that your child has been infected with meningococcal disease, be sure to notify your family physician right away so that he can treat your child as soon as possible.
If you think that your child might be suffering from meningitis, he should be evaluated by a doctor right away. An examination is necessary to check for any signs of meningitis, which can include fever, headache, fever in the upper chest, or yellow to red throat. A swab of the throat may also be tested for meningitis. A CT scan may also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Symptoms of meningitis generally occur at night. The most common symptom of meningitis is fever. In infants, fever, weakness, and lack of appetite are also common.
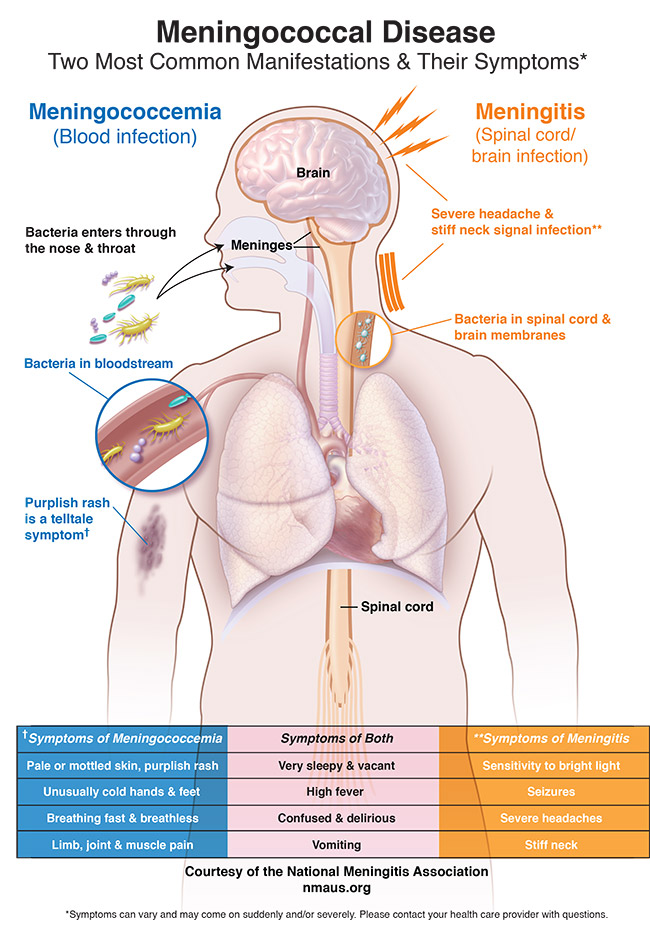
Other common symptoms of meningitis include swollen lymph nodes, vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, fever, and diarrhea, but these symptoms can also occur in adults. When these symptoms do not go away on their own in a few days, it is best to see a doctor. Some symptoms can be treated with antihistamines. If symptoms of meningitis occur at night, your child may experience: pain or tenderness around the ears, facial swelling, fever, coughing, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can be relieved by rest or an oral antibiotic.
If symptoms of meningitis occur, your doctor will be able to tell if your child has contracted the disease through a cough or sneeze or if he has come in contact with the bacteria. If your child develops symptoms of meningitis after having been in the hospital, he may be suffering from otitis media. Otitis media is a complication of meningitis and the bacteria may have traveled up to his brain and caused a secondary infection.
Symptoms of meningitis usually develop within two days
The majority of cases of meningitis will clear up on their own without treatment. However, if symptoms of meningitis do not clear up on their own, you should seek medical attention immediately.
If you suspect that your child has been infected with meningitis, you should see your doctor as soon as possible. If symptoms of meningitis continue after two weeks, then you should get your child tested for meningitis.
If symptoms of meningitis do not improve within one week, then your child's case of meningitis is more serious than just a cough or cold. It may be a sign of more serious complications like meningitis. Although the child will be tested and treated initially for the cough or cold, if it recurs after two weeks, your child should be evaluated for meningitis.
A doctor can perform tests to confirm that the child has been infected with the bacteria that causes meningitis. The results of a CT scan will help your doctor determine whether your child has contracted meningitis. The results of a scan will help confirm the diagnosis of meningitis. If your child does not improve within four weeks, it is time to see your doctor. If symptoms of meningitis have not improved after two weeks and your child is diagnosed with meningitis, then your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat the symptoms of meningitis and prevent the infection from worsening.