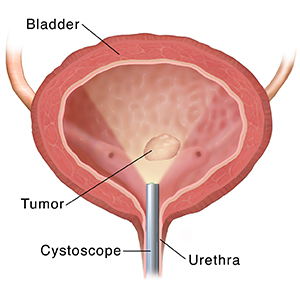
Bladder cancer is the second most common cancer amongst women after breast cancer and is a very aggressive disease. It mainly affects men, but it is becoming more common in women as well. Bladder cancer occurs when the DNA from healthy cells in the urinary bladder changes or mutates, causing the normal functions to malfunction.
Bladder cancer can be diagnosed at any stage, but it tends to strike later in life. This makes it difficult to cure because the disease is often very slow growing and there is no noticeable symptoms. However, bladder cancer has a few symptoms that can be easily detected if it is found in early stages, before it spreads to other parts of the body.
Bladder cancers are usually not fatal, but they can have serious consequences, such as a bladder obstruction, abscesses, blood clots and other serious complications. In most cases, the symptoms are caused by the presence of bacteria or other pathogens in the urine. This may result in blood or urine spotting or urination in unusual ways. Other symptoms include painful urination and a feeling of fullness.
Bladder problems are very common in both men and women. It is estimated that nearly 70% of all people will experience some type of incontinence in their lifetime. The bladder is responsible for collecting urine from the body and storing it for disposal, as well as moving urine from the kidneys to the bladder for excretion. However, some people do not store urine properly, and this leads to infections and blockages within the urinary tract.
When bladder cancer occurs, the symptoms become much worse than they would be otherwise. As the cancer begins to spread to other organs, the symptoms can become quite complicated. It is important that you seek medical attention if you suspect that you have bladder problems. Although there is no cure for bladder cancer, doctors can use various treatment options, ranging from surgery to chemotherapy. Surgery is usually recommended for people with advanced bladder problems and is rarely used for people with bladder problems who have not yet developed the cancer.
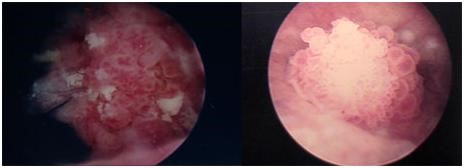
There are several treatment options available. Surgery for bladder cancer generally involves removing the bladder and/or urethra and can be performed on an outpatient basis under general or local anesthesia. However, surgery can have severe side effects and is not usually covered by health insurance plans. Chemotherapy is usually the preferred form of treatment for bladder cancer because it has fewer side effects and is often administered on an inpatient basis.
Chemotherapy is also used to prevent recurrence. Chemotherapy drugs kill cancerous cells by producing chemicals that stop them from multiplying. It may also increase the amount of urine that is passed through the urine stream, stopping the growth of bacteria within the urinary tract. Chemotherapy drugs work in two ways: by increasing the amount of urine that is produced and increasing the amount that is eliminated. Chemotherapy drugs may also inhibit the ability of some types of bacteria to produce enzymes that help to break down proteins.
It’s important to note that there are no guarantees against bladder cancer, but there is a lot you can do to protect yourself from developing it. You should avoid smoking and never engage in strenuous physical activity for an extended period of time, especially activities such as jogging or contact sports for an extended period of time, as these activities place a strain on the urinary tract. Exposure to harmful chemicals such as smoke, harsh chemicals, cleaning products and gases can also contribute to bladder problems.
Women who wear underwear above the knee or below the knee are more likely to develop bladder cancer due to the extra pressure on the urethra. It is important to wear smooth and breathable clothing. The most common form of cancer that occurs in the bladder occurs when a person excretes urine that contains small particles of debris.
Women who wear thongs or have a habit of wearing low-heeled shoes may have difficulty urinating or contain small particles of debris that can become lodged in the urethra. These women are at greater risk for bladder problems. Some women with kidney disease or diabetes are also at risk of bladder problems. If you suspect you have a bladder problem, it is important to discuss your concerns with your doctor or gynecologist so that he or she can refer you to a specialist. for further testing and / or treatment.
A person’s age and gender play a role in whether they are at greater risk of bladder cancer. Younger people have fewer bladder problems than older people. However, men and women of any age who are experiencing bladder problems should visit their doctor and check their health website fitzpatrickperio.com
for more information to make sure there is no serious cause. Doctors also believe that people who are overweight or obese may be at a higher risk of bladder cancer.